Minimise risk and bolster client confidence with Docuten’s biometric signature

What is a biometric signature?
One of the types of digital signature available through Docuten is the biometric signature.
A biometric signature enables documents to be signed digitally by executing a handwritten signature on a device with a touch screen (such as a tablet or a smartphone) that records the biometric information of the signatory. Biometric information is unique and different for each person, thus guaranteeing the identity of the signatory.
Use cases
In an effort to best adapt to diverse use cases, Docuten offers two ways to sign biometrically:
- Biometric signature using the Docuten app for signing biometrically.
- Biometric signature on the web, which does not require any app to be installed on the device.
In this way, Docuten’s biometric signature adapts to a variety of different client needs: if they prefer to use their own device in person to get a document signed digitally with a biometric signature, or if they prefer to forward the document so that the signatory can sign biometrically on their own device.
For each use case, Docuten offers different types of signatures that enable our clients to digitally sign all kinds of documents with employees, clients or vendors.
Security & confidentiality
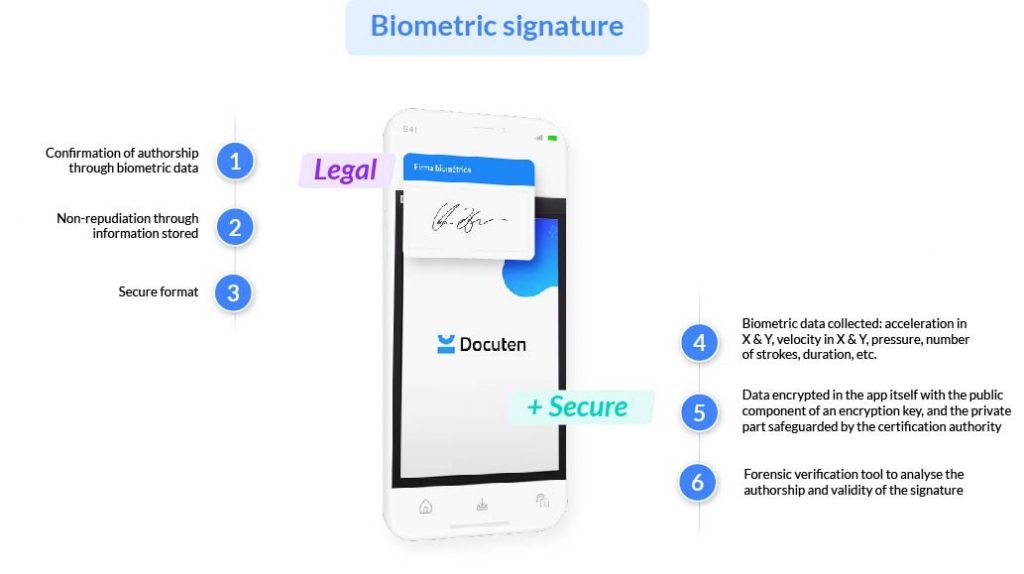
When a document is being signed biometrically, Docuten records the biometric data. This can include the number of strokes made, their starting and ending points, the speed of each stroke on the X and Y axes, the angular speeds, etc. All of this information, if called upon in a judicial process, will allow a handwriting expert to determine whether a particular person has signed a specific document.
The recorded biometric information is stored securely and exclusively within the digitally signed document itself. It is encrypted and stored using the ISO 19794-7 standard to enable the future interoperability of this data with forensic verification tools, and Docuten also has its own forensic verification tool.
Biometric information can not only be used to identify a signatory at any given time, but the information is secure as it is not accessible or usable in any way. In the world of biometrics, it is as important to safeguard the privacy of biometric information as it is to take advantage of its ability to identify people.
Only under judicial request and authorisation would it be possible to decrypt biometric information included in a digitally signed document. A private decryption key safeguarded by a qualified provider that issues independent certificates would have to be used.
Legal validity of a biometric signature
A biometric signature executed using Docuten’s technology electronically gathers unique biometric data from each individual to securely associate them with the content of a digitally signed electronic document. As such, it fulfills the legal requirements for an advanced electronic signature established by article 26 of the eIDAS Regulation, which regulates electronic signature for documents in the European Union. Docuten’s biometric signature fulfills the established requirements since:
- it is uniquely linked to the signatory;
- it is capable of identifying the signatory;
- it is created using electronic signature creation data that the signatory can, with a high level of confidence, use under his/her sole control; and
- it is linked to the data signed therewith in such a way that any subsequent change in the data is detectable.
In other words, a biometric signature executed through Docuten guarantees that an electronic signature has been done by a specific person, that this person can later be identified, and that this biometric identification is uniquely linked to a particular document. The digital signature ensures that the content of the document cannot be modified later, which includes the encrypted biometric information.
Forensic verification tool
To bolster legal security for our clients, Docuten has a forensic verification tool that can be used by a handwriting expert in litigation.
This tool allows the handwriting expert to compare signatures and analyse their authorship, once they have been decrypted.
In the event that a signature is contested, a formal request will be made involving the provider that safeguards the decryption key, and all of the parties concerned must come forward for the process. This prevents one party from possessing all of the elements involved with the intention of improper use.
The process begins with the original signed document where the encrypted biometric information is contained. It goes through a script that extracts the information from the document in the form of a file, and is decrypted by the independent qualified provider.
Once the biometric information is decrypted, one of the first steps is to identify where the signature was done, since the handwriting expert will carry out analyses using the same conditions in which the signature was made.
Usually, at least five signatures are needed to have enough information to compare with the signature being analysed.
The verification tool compares the different aspects of the signature, from pressure, speed or time, to a video showing how each signature was done. Through an algorithm, the tool also analyses the percentage the signature in question matches with a confirmed signature from the same signatory.
In the video below you can see how the verification tool works, including the comparison between speed and time as well as the percentage of shared traits for the example presented.
